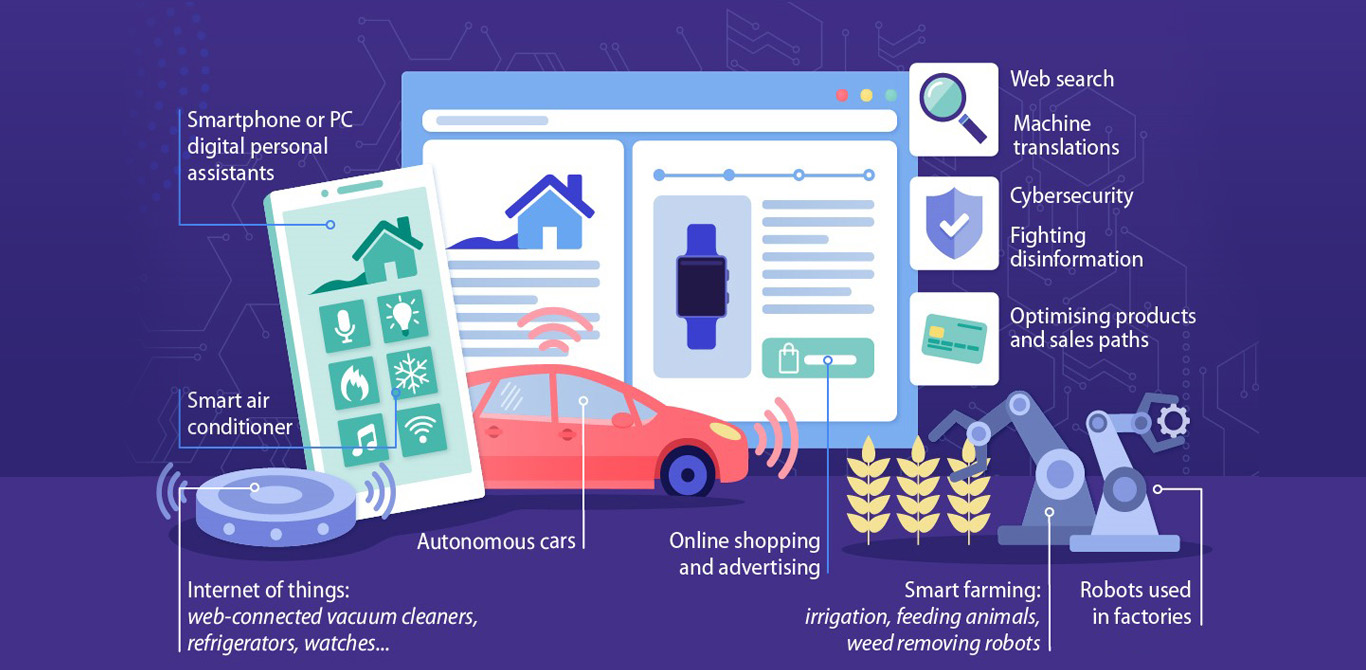
In today’s world, Artificial Intelligence has become pervasive in our daily lives. AI is with us everywhere and helping us with many consumer and industrial use cases, as shown in the figure below – right from reading our sleep patterns on our smart wearables to the tagging of the content we read on social media to driving our cars to personalizing our online shopping etc.
Intelligent personal assistants like SIRI, CORTONA, and ALEXA have become popular household names, cutting across cultural and generational boundaries. After getting its foothold with consumer apps, AI has penetrated every primary industry, such as retail, healthcare, banking, automotive, insurance, etc. The application of AI technology is rapidly increasing in every vertical sector.
AI is Everywhere
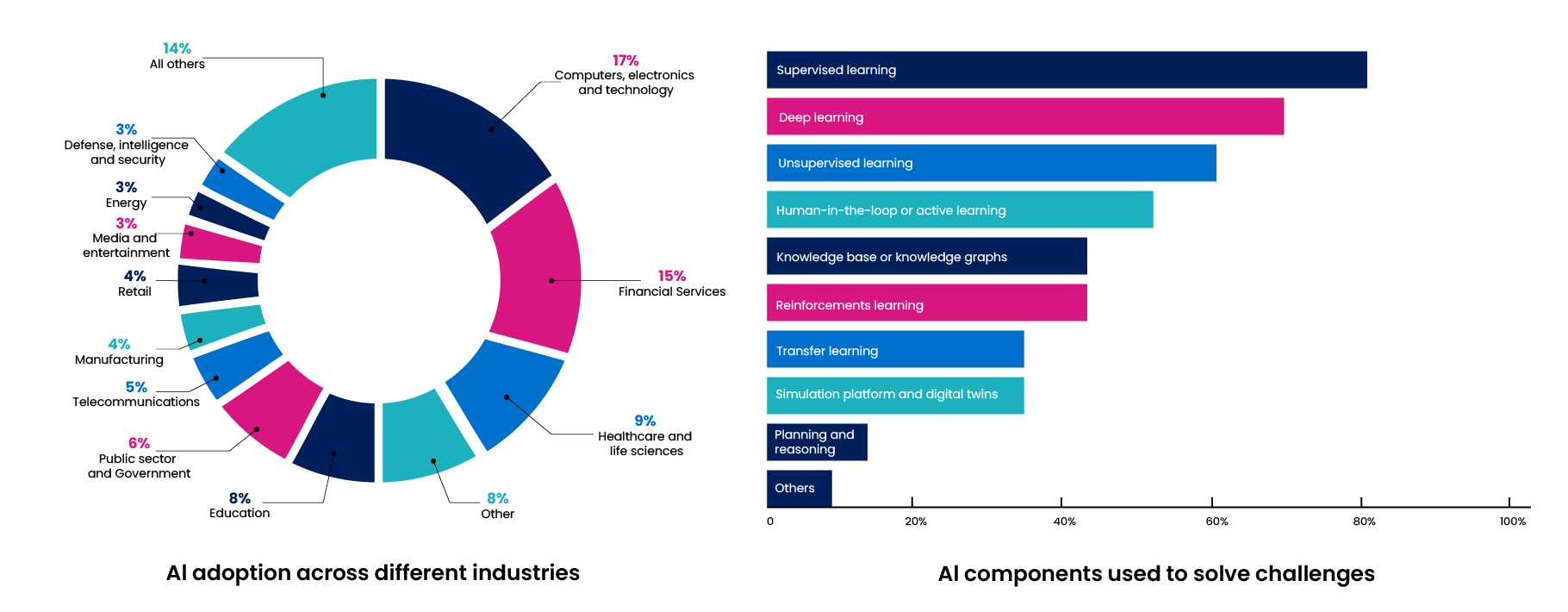
While AI no doubt has been proving to help improve human productivity and accuracy, we have to wonder if it will ever come close to the sophistication of natural intelligence vs. remaining artificial with its many limitations. Can it ever predict insurance claims accurately? Can the AI in a self-driving car be calibrated enough to accurately differentiate between a man/woman/old/disabled? Can we see the social media feed that genuinely interests us? And most of all, is AI capable of incorporating the critical thinking skills of humans? Or, are we just getting busy building something fancier and fancier, which may make us more vulnerable? These are essential questions we must answer first as we move forward with the AI roadmap and broader adoption. As shown in the figure below illustrates the growing adoption.
AI Statistics of Usage Across Industries & Applications
With the rapid advancements in Machine Learning and Deep Learning and the supply of Big Data that is needed to train the respective models to be more accurate, AI may very well close some of the cognitive gaps compared to natural intelligence, but what about the faculties of critical thinking?
Critical thinking manifests itself in ethics, morals, social values, and emotional regulation. These human virtues help us in deciding what is right or wrong. Integrating these virtues into AI is crucial for it to be sensitive, responsible, and intelligent.
What is Ethical Dilemma in AI?
Current efforts focused on building human-like machines (humanoids) face a challenge in fully understanding the gamut of use cases related to virtues that AI algorithms should be trained on. We also have to wonder if we have all the datasets required to build an ethical AI model. As shown in the figure below lists a set of questions that collectively represent the dilemma
we face in this regard.

- What is use case Al wants to solve?
- What datasets used for training Al models?
- What are the assumptions and potential biases of Al model?
- Does the Al models are explainable and justifiable?
- Does Al solutions consume any sensitive or personal data?
- How do you protect the data loss or tampering at all levels of Al lifecycle?
- Did we include a Human Expert in Loop for evaluation?
- Who gives the sign-off and on what parameters?
- Who is getting impacted / benefited / making wealth from the Al solution?
Addressing these questions can strengthen an AI engine, making it more human-centric than job-centric. But how do we handle these questions?
While there have been many schools of thought around AI ethics, here are a few principles in AI ethics that can help us resolve the dilemma.

Fairness
Ensure that humans are treated fairly by the machines. The machine learning models have to be tested for sample bias, representation bias, behavioral bias, popularity bias, gender bias, regional bias, etc.,

Reliability and Safety
Reliability and Safety are the most significant parameters that build trust in a model. An AI Engine should be able to perform as per its original design. Any deviation/manipulation from the purpose may revoke the belief in an AI engine.

Privacy and Security
In the wake of building connected devices and smart devices that store fingerprints and sensitive data, there is an increasing level of concern about the security & privacy of data. Building an AI engine should also demonstrate an organization’s security and privacy framework in protecting its users’ data. AI can benefit humanity only when it upholds security and respects privacy.

Inclusiveness
Developing an AI process that involves people from various walks of life, from different geographies, gender, age, etc., can help build an engine that can lead to social harmony.
Transparency
An explainable AI is a transparent AI. AI engines built for social or individual impact should be a “white box” understandable to humans. When it comes to transparency in ethical AI, organizations must take responsibility for their AI-based engine’s decisions.

Accountability
Introducing accountability in AI processes again contributes to building trust. Accountability in AI doesn’t just mean ensuring the proper functioning of AI systems and safeguarding AI against unintended uses.
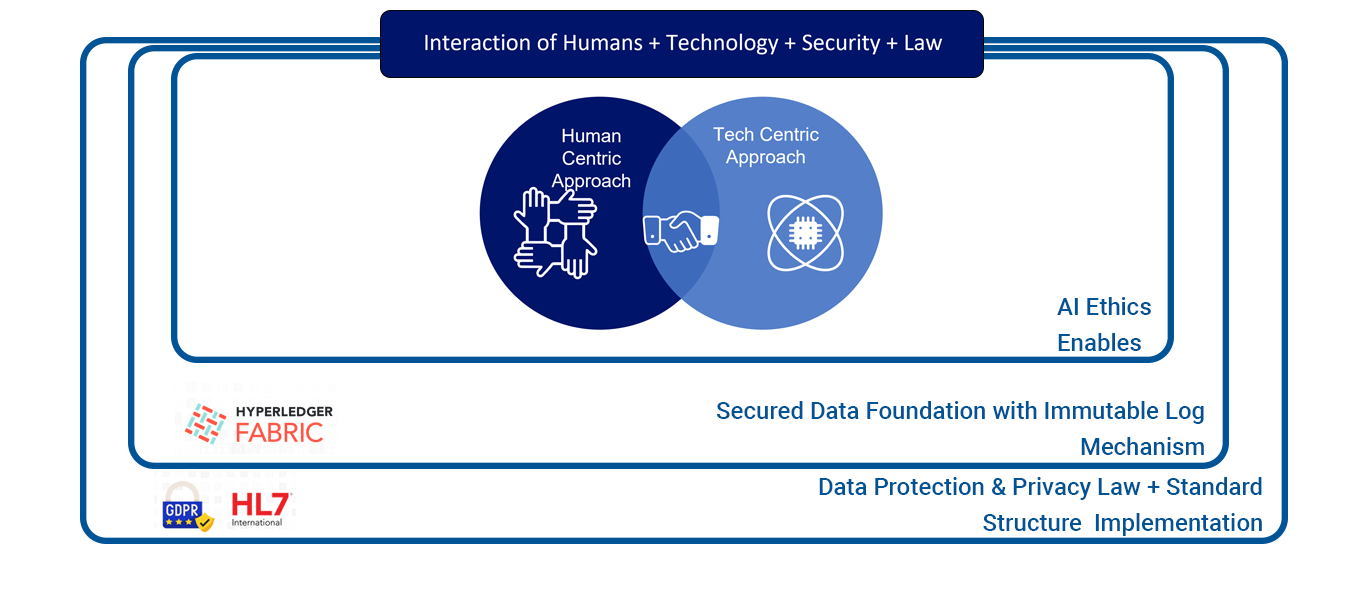
AI Ethics Framework
Creating a good AI ethic framework is crucial for designing and developing comprehensive AI systems. It highlights the benefits and risks of AI tools and establishes guidelines for their responsible use. The practical framework is prepared by incorporating micro and macro enablers, including human inclusiveness, tools for fairness advancements, immutable data systems, and data protection laws, as shown in the figure below.
AI Ethics Practical Application Framework
Practical pursuit of Al Ethics requires human inclusiveness, fairness tool advancements, immutable data system and imposing the data privacy law. By applying these micro & macro enablers we have prepared the below practical framework.
Addressing ethical questions can strengthen AI engines, making them more human than job oriented. So, how do we handle these questions?
While there are many schools of thought related to AI ethics, here are a few principles that can help us resolve the dilemma.
The Framework Includes the Following Key Enablers
Interaction of Humans
Even after all technological advancements, AI still needs human intervention. There are not enough experiments on human-robot collaboration models that will produce accurate results with the same efficiency to meet expected results. Scientists and researchers are developing new innovative ways to automate activities in our daily lives; AI still needs human intervention to perform efficiently.
Human Centric Approach
Human in the Loop is the best approach for measuring the responsibility of the technology to the citizens, community, and customers. In this approach, we shall rely on a combination of cross-functional resources to measure the impact of the Al use case and the fairness in developing the solution.

This approach is considered the best for measuring the responsibility of the technology AI systems learn by observing humans dealing with real-life work and use cases as shown in the figure above. Human-in-the-Loop (HitL) and Conversational AI are examples of how the human-centric approach supports AI systems in making better decisions.
Ultimately, the goal is to get unbiased results and ensure that the AI ethics fairness report standards are met.
Technology
This aspect of AI focuses on building the AI fairness evaluation tools used to verify the algorithmic bias and ethical risks in AI decision processes based on machine learning data models. As shown in the figure below illustrates how We must include appropriate data validation, model interpretation, and fairness tools to ensure this.
Technology Centric Approach
It’s time to invest in Community-Driven projects for building the Fairness Evaluation Tools that can mitigate the ethical risks of data manipulation and untangle the black-box machine learning models.
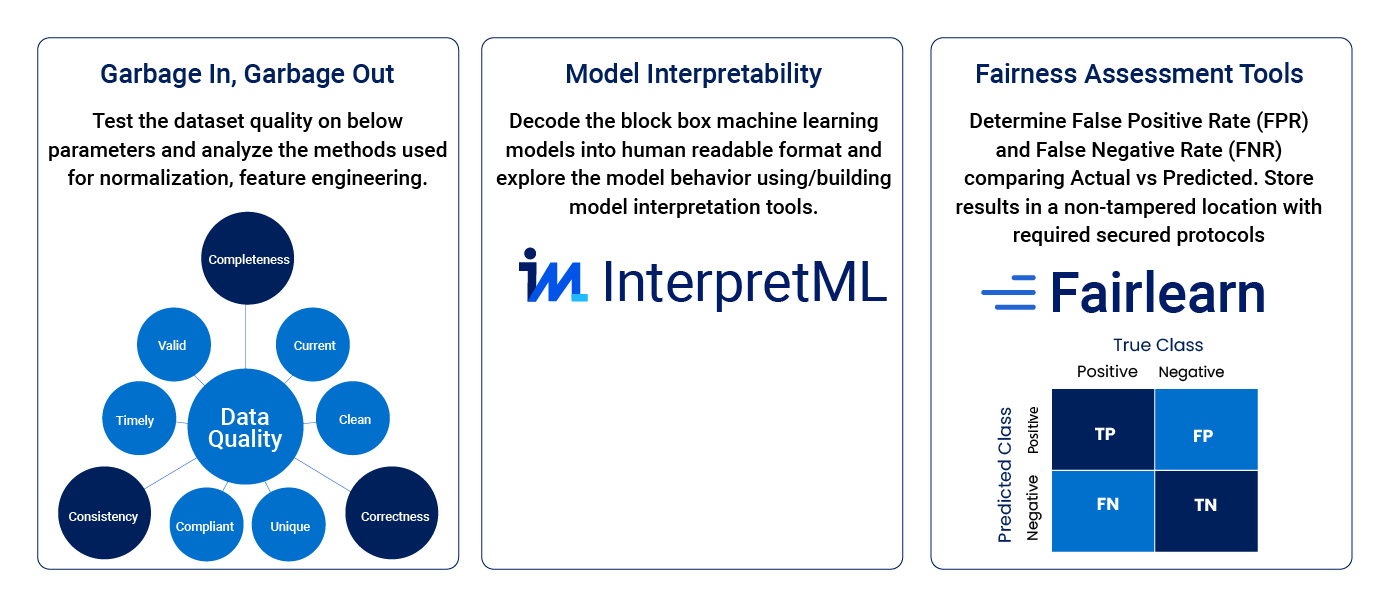
- With Big Data coming in variety, volume, and velocity, it becomes imperative that a proper data validation mechanism be incorporated to ensure the quality of input data is used for developing models and insights.
- Model interpretation is an essential part of AI ethics as this is where the algorithms continuously learn from human input data to create machine-labeled outputs.
- The last but critical step in the techno-centric approach is the fairness assessment tool. This step ensures that there is no algorithmic bias in the results from the AI process. Standards in AI ethics provide tools to enable you to detect the presence of bias in your data model or output.
Security
The applications of AI without human intervention may lead to serious security lapses and vulnerabilities. The data repository on which the AI model is built can also be hacked, teaching the AI to believe or understand it the way the hackers want. The core data can also be diluted to give AI wrong calculations and impressions. This can lead to severe consequences for humankind itself.
Building the Secured Data Foundation for AI
Establish a resilient Single Source of Truth system that can prevent Security Breach, Data Theft, and an immutable Blockchain-based Log Monitoring mechanism that tracks all CRUD operations.
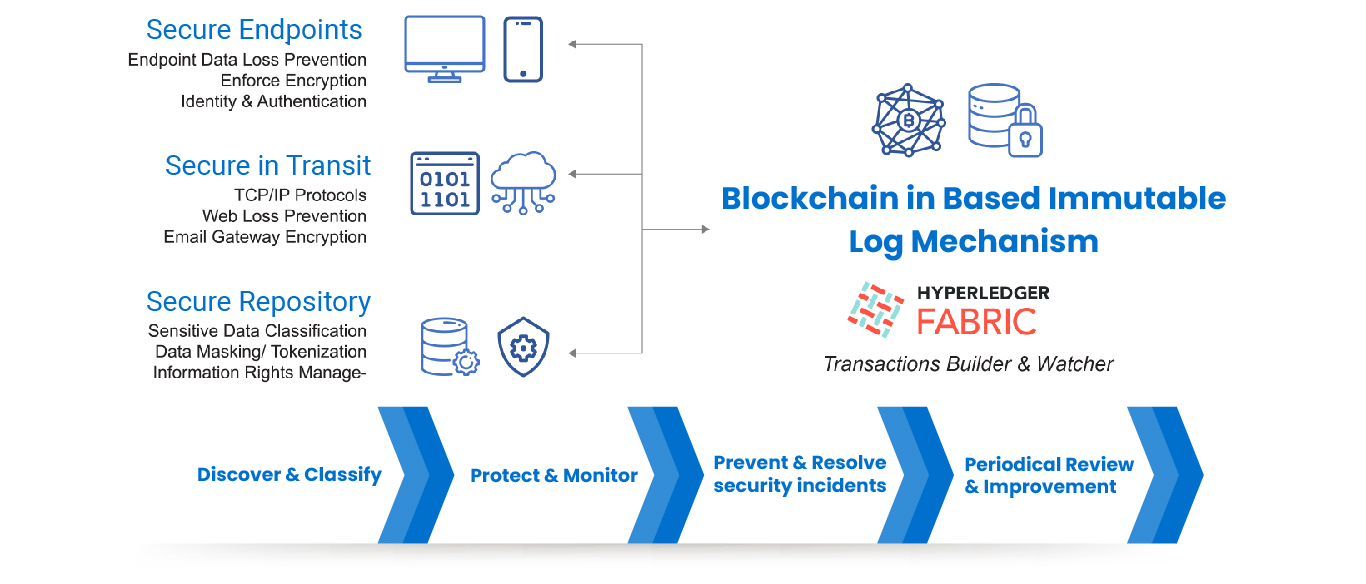
Privacy and Consent Laws
While a lot has been done for data security and fair usage, the same cannot be said about AI, as there is no piece of regulation to ensure ethical AI is enforced. Finally, AI is as good as we create or model. Even with restrictions and informed use of consent, it is fair to say that just like humans have found a way to find loopholes and access private data, AI can also manage to do the same. More easily so, thanks to a much more complicated and broader virtual network of social media. Current laws must be updated and made more stringent to curtail mismanagement of data privacy.
In closing, many efforts are underway to take ethics in AI a step further towards application from abstraction. These efforts include taking a HitL approach, making AI more transparent, implementing fairness in training the engines, and overall making it more human-centric than just a job-centric AI. A responsible AI can add significant value to the next generation of users.
Rewrite the Data Laws established before Smart Phone Era
Write and impose a consistent Data Protection, Privacy and Compliance law across the states similar to the EU GDPR Compliance law. It protects sensitive information against unauthorized processing, accidental loss and destruction.

Boundaries must be set in AI where it cannot move beyond a certain level to access or use data. We must establish common Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) standards when dealing with personal, sensitive, and community information to protect data from unauthorized processing and dissemination.
With technology evolving at a faster pace, and the line blurring between the Digital and physical world, we need to focus on Ethical governance and public policy changes to govern and manage the advancement in Digital People Technologies and mitigate the risk related to Deepfake technologies to both People and Society.
About the Author

Umesh Udayaprakash is a passionate technology evangelist and information technology executive. He has over 21 years of experience in strategic planning, devising IT roadmaps, service delivery, and improving efficiencies.
Umesh currently serves as the Vice President of Delivery at Innova Solutions India Private Limited, a global information technology company combining a global reach with a local touch.
Umesh strongly believes in “Learning is Growing.” He is pursuing his Ph.D. in Artificial Intelligence, closely studying its impact on ethics and public policy-making space.


