Table of Contents
1
Introduction
2
Telehealth – The Concept in Focus
3
Types of Telehealth
4
Why Telehealth?
5
Market Model and Forecast
6
Telehealth Application Checklist
8
Case study: Fully Integrated Telehealth Product Creation
9
Conclusion
10
Contributors
Introduction
Introduction

The COVID-19 pandemic has compelled people worldwide to adopt alternative ways of doing everyday things like buying groceries from a busy supermarket or maneuvering the heavy traffic to reach the office daily.
US healthcare has been long-suffering from rising costs and lack of timely care coordination. Ideally, well-executed preventive care can reduce a large number of hospitalizations and high-cost treatments. However, in reality, the adoption of preventive care is still in its nascent stages. Telehealth allows patients to regularly connect with doctors and healthcare providers in a far more hassle-free and cost-effective manner. It goes beyond a simple remote consultation or an outpatient visit, making Telehealth quite a potent tool to offer large-scale preventive care at significantly reduced overall costs.
Telehealth - The Concept in Focus
Telehealth – The Concept in Focus
Telehealth involves the use of electronic communication systems, software to monitor and treat patients instead of or supplementing physical office visits. In the pre-COVID world, telehealth was considered a rapidly growing yet secondary alternative to a physical visit to a healthcare provider. The COVID-19 pandemic, however, has changed this perception quite to a great extent.

Telehealth has now emerged as both a short and long-term option competing with regular in-person visits to the doctor’s office. Interestingly, telehealth is rapidly being accepted as the most feasible and comfortable option for both patients and providers.
In this white paper, we will discuss the evolution of Telehealth to the best alternative, which allows timely care for the patient in need and lifts the barriers in the adoption of preventive healthcare. We will also discuss the integrated approach that can align your digital strategy to create Telehealth products across all platforms.
Types of Telehealth
Types of Telehealth
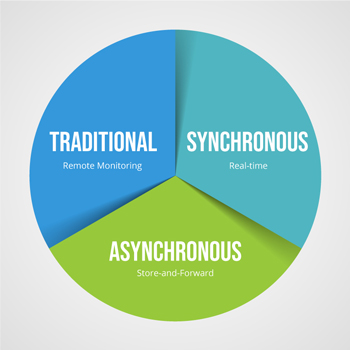
With the evident benefits of virtual health services, new practice areas have emerged, which can be broadly categorized into – Traditional, Synchronous, and Asynchronous.
Traditional
Remote Patient Monitoring or Telemonitoring is the conventional method that allows healthcare professionals to track patients’ vital signs and activities remotely. This type of setup often benefits the patients in rural areas, recently discharged patients or even those in long-term care conditions. Remote monitoring is also extremely useful in treating chronic conditions like diabetes and heart diseases, among others. For example, tracking glucose levels and sending data to doctors can be self-managed by elderly patients from home or assisted living facilities conveniently and with less out-of-pocket costs.
Traditional
Remote Patient Monitoring or Telemonitoring is the conventional method that allows healthcare professionals to track patients’ vital signs and activities remotely. This type of setup often benefits the patients in rural areas, recently discharged patients or even those in long-term care conditions. Remote monitoring is also extremely useful in treating chronic conditions like diabetes and heart diseases, among others. For example, tracking glucose levels and sending data to doctors can be self-managed by elderly patients from home or assisted living facilities conveniently and with less out-of-pocket costs.
Synchronous
AKA real-time telemedicine, is a telehealth approach that started late in the market but is now the most popular. This real-time video/digital visit facilitates a virtual imitation of a regular patient-provider visit setup like a clinic or a hospital. These real-time telemedicine encounters utilize video conferencing software to see and hear each other. It is popular for primary care, follow-up visits, and the management of medications. It is to be considered that the Telehealth encounters should be conducted using technologies that protect patient privacy while meeting the strict patient protections required by the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
Asynchronous
Often known as Store-and-forward, this method is suited for remote places that are poorly connected with the rest of the world, where care delivery is of great concern. In this method, the healthcare providers share patient medical information like lab reports, imaging studies, videos, and other records with a physician, radiologist, or specialist at another location. It is not unlike email, but it is done using a solution that has sophisticated built-in security features to ensure patient confidentiality. This approach enables enhanced collaboration among providers than traditional methods, even across different geographies and time zones. This approach is particularly popular for dealing with treatment and diagnoses involving certain specialties, such as dermatology, ophthalmology, and radiology.
Why Telehealth?
Why Telehealth?
Telehealth intervention, which enables more regular health checks and monitoring, can lead to early detection of ailments. This, in turn, can help avoid ER visits, suffering for patients, the strain on patient and system spending, and facilitate better treatment plans.
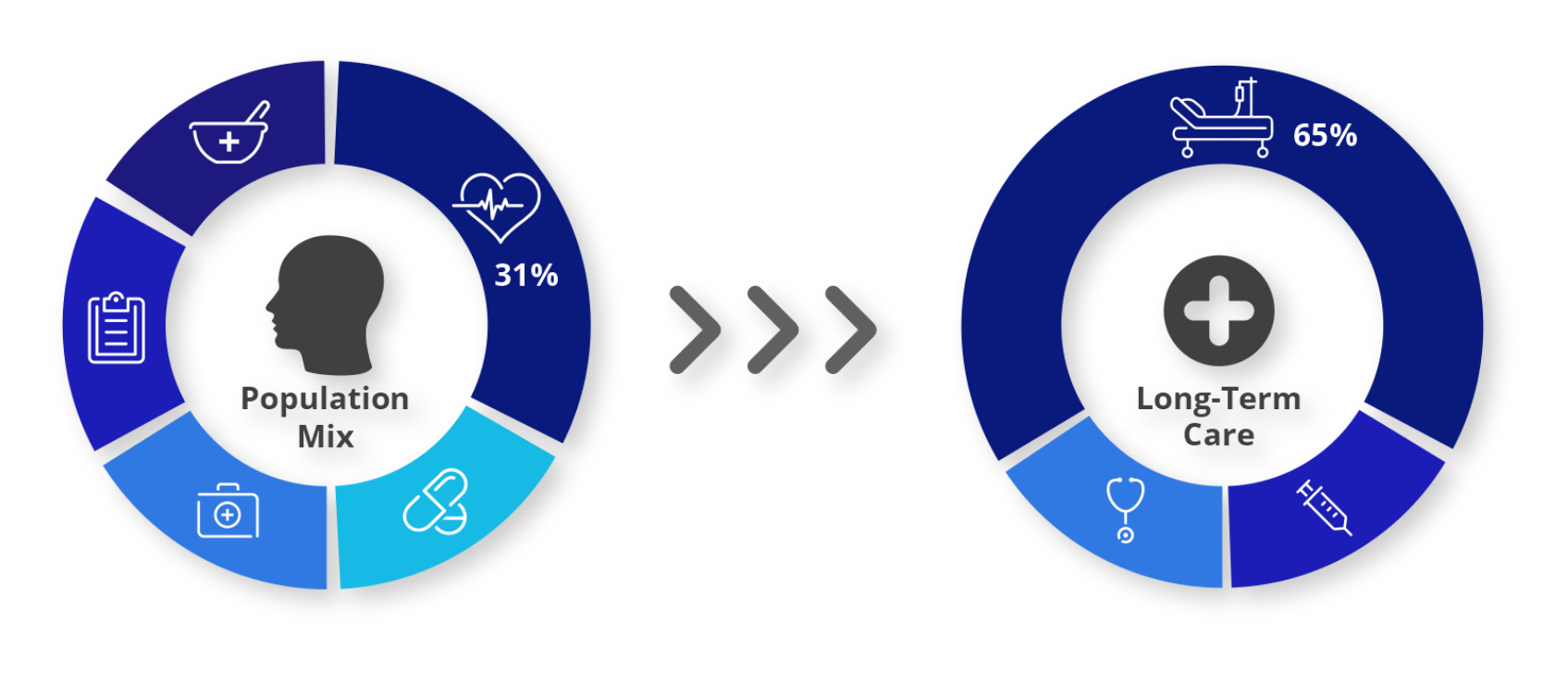
One of the main concerns for healthcare systems in most developed countries, including the United States, is the aging population. A growing aging population results in dipped revenue and a higher percentage of people requiring Long Term Care (LTC). A report suggests people with LTC needs in the US make up 31% of the population but account for 65% of all outpatient visits. Not just LTCs, longer stays at hospitals is also a concern as this would cause an economic burden on the system while also resulting in lower availability of beds for others. Telehealth services can replace outpatient visits and provide remote patient monitoring services for people with LTC needs.

From the government regulations standpoint, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) is doing away with parity laws. Earlier only ten states had the reimbursement plans of Telehealth on the same amount for outpatient visits. But, with the current announcements, policy changes, and evolving ecosystem – Telehealth is proving to be a great bet for providers as well.
The emphasis on value-based care in the evolving healthcare ecosystem is sending ripples of care redesign. At the same time, the care delivery model is closely knit with the presence of defined care processes integrated around Telehealth. Patients’ experience in identification and referral through risk stratification, their adoption, and response to the technology will define future involvement.
Digital healthcare services are built on virtual networks, which in other terms can be referred to as expertise availability on one single table by enabling scale. The patients can access better opinions across the network. The wellness industry has evidently begun to rise from the beginning of this decade and is estimated with a value of USD 12.4 B (Grandview Research, 2018). The high street pharmacies are readily offering health monitoring or measuring devices like electronic scales, blood glucose monitors, blood pressure monitors at a mass-market consumer-level price. All of this points to the level to which the industry has geared up. Of course, we should point out that this wellness market is proving to be a driving factor in lowering the costs of telehealth services primarily for patients in levels 1 and 2 of Kaiser’s Pyramid of care model.
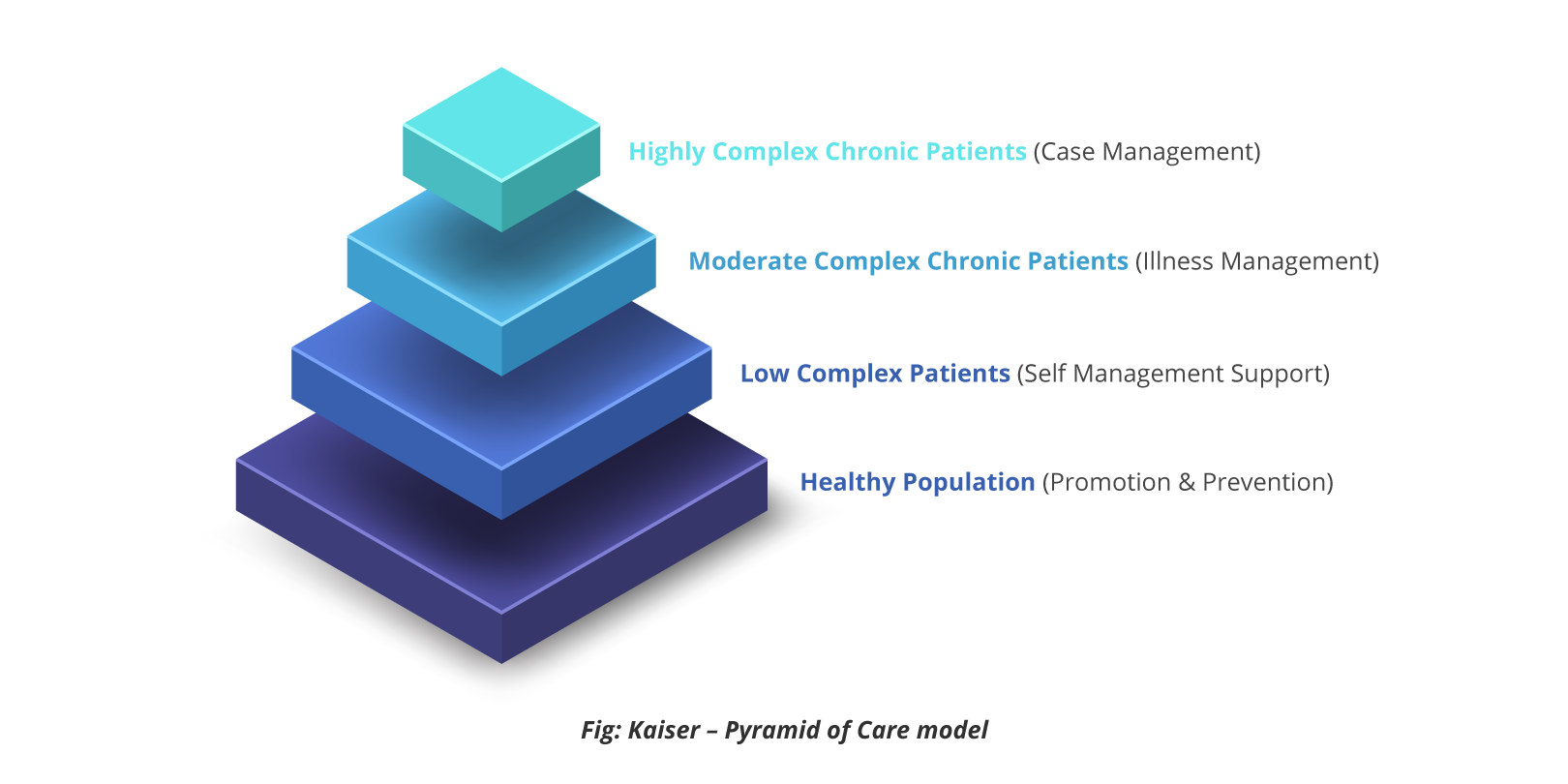
Telehealth services make patients’ lives better with benefits like – improved and effective daily self-care, increased satisfaction with quality care, reduced levels of anxiety, fewer stressful/unplanned admissions, and more importantly, less travel for routine checkups. In parallel, better medication compliance, reduction in unnecessary physician visits, promoting pro-active case management with early intervention and prevention, and lower caseload per nurse would constitute the fair share of improvement for primary care units.
At large, the health system would benefit significantly by reducing the strain on budgets, meeting LTC growth within available funds, planning better for demand, and personalizing appropriate care. The only foreseeable concern lies in pushing traditional setups for technology enablement
Market Model and Forecast
Market Model and Forecast
The Telehealth offerings through information technology services fall into two buckets. The first can be called Application and System Development, and it encompasses video interface applications, remote patient monitoring systems, remote devices, and vitals sharing. The other model can be termed Tele Consultations, and it includes video/audio calls, Store-and-forward communications, and other communication platforms.
The existing models in which healthcare professionals can utilize Telehealth services are – large provider groups, EHR vendors, practice management vendors, self-insured employers, payer and TPAs, health tech companies, diagnostics centers, and individual members.
However, the post-COVID needs have significantly metamorphosized care delivery worldwide and have caused a massive spike in the adoption of Telehealth services. The US markets are spear-heading the market strengthening for Telehealth services. Various recalibrated market research reports suggest that Telehealth services’ global market is expected to touch USD 80 Billion by 2025.
Telehealth Application Checklist
Telehealth Application Checklist
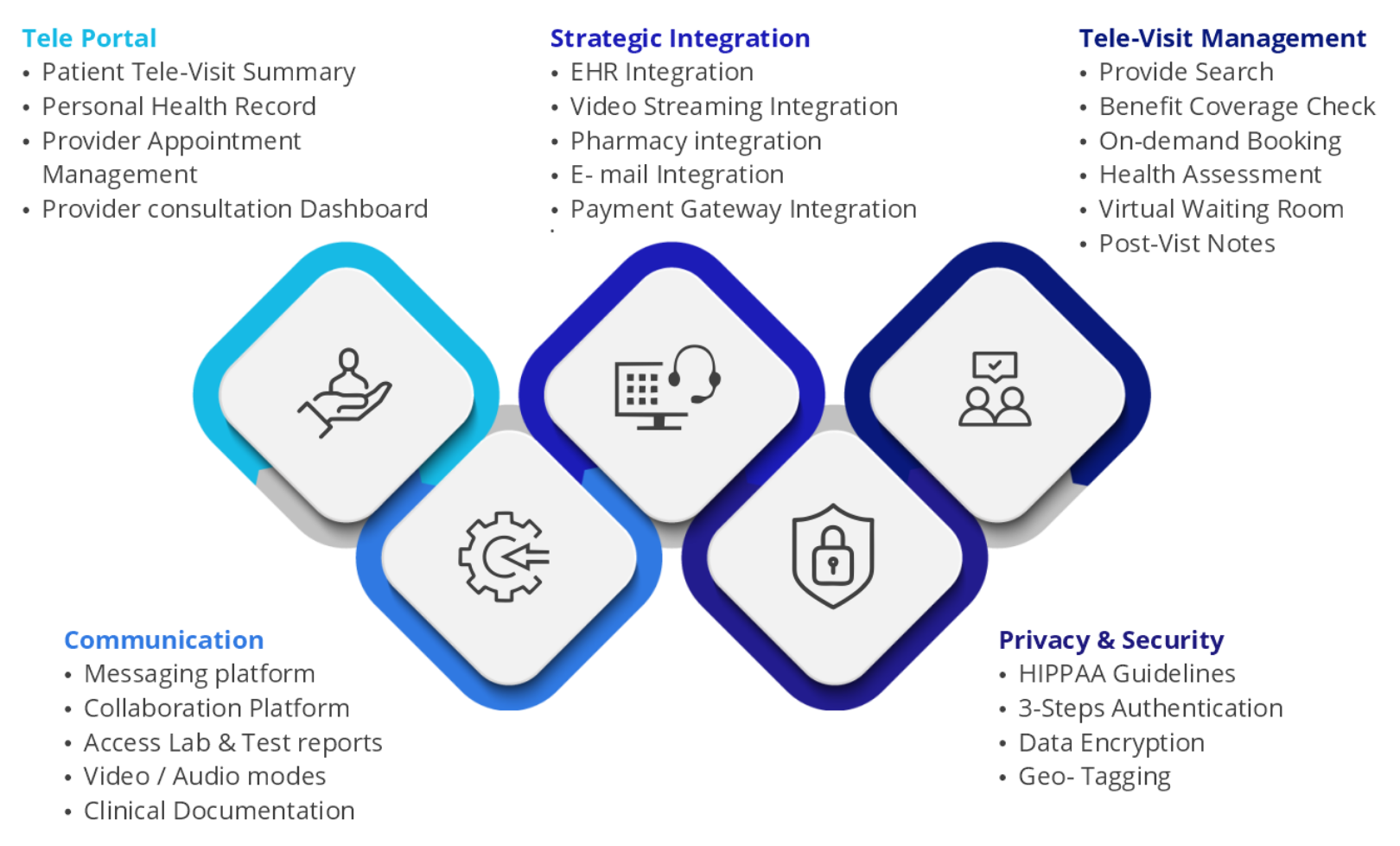
With substantial competition in the market to gain Telehealth share, it is critical to understand which features are relevant and which can act as differentiators. The following diagram provides details about key modules that every Telehealth application should contain to compete with existing market leaders in Telehealth from the new product development perspective.
Proper hardware and connectivity are crucial to seamless teleconsultation. With proper connectivity and the right device, patients and providers can benefit from the range of features these apps have to offer. Telehealth platforms, today, are getting increasingly convenient features to support multiple functions in the care delivery cycle such as:
- Easy access to patient’s health summary
- Storing necessary health record
- Easy management of provider appointments
- Easy maintenance of the facility’s activitie
- Integration with third-party applications like EHR records, payments gateways, pharmacies, marketing activities, and even the next-gen wellness IoT devices.
Telehealth platforms should be built following HIPPA guidelines, have a multi-stage authentication mechanism for patients and providers, secured and encrypted data transfers, and geo-tagging that enables or restricts accessing the application based on the geographic presence of the user
Technology Assessment for Telehealth
Technology Assessment for Telehealth
For a more scalable application, Telehealth requires choosing a secure and cutting-edge technology stack. The development of telemedicine apps involves in-depth technical expertise and extensive knowledge of data compliance. Native mobile apps on iOS and Android platforms are critical to capture an expansive customer base. However, web applications are required for providers to offer virtual consultations as provider offices typically use tabs and desktops.
The most important tools and accelerators used in Telehealth software development
WebRTC
These technologies are used to develop app features like video calls, video chats, screen sharing etc. WebRTC is an open-source project that provides mobile apps to have real-time communication via APIs.
Twilio
A software that is used to add video and video messaging along with the notification and reminder options in an app.
Google’s Geolocation API
Implementation of Google’s geolocation API helps the app in fetching real-time location data of the user.
Stripe
Payment integration is one of the most vital aspects of a Telehealth application. One such product helping secure payments is Stripe. Stripe provides APIs which can be used to integrate the software into the app and use it for payments. It helps in accepting payments from various payment sources like debit cards, credit cards, PayPal, etc., based on the app’s requirement and the location of the app user.
Firebase
Enables continuous push notifications so that message broadcast can be sent seamlessly to all available providers simultaneously
Artificial Intelligence
Most healthcare apps use the power of AI to enhance user experience. Chatbot feature can be built using AI, which can help patients get answers to most of their queries faster and at any time of the day through FAQs that are researched and embedded into the application. The app can also use natural language processing (NLP) to improve the machine learning process to help patients find answers to most asked queries
Cloud storage
To access and store data from anywhere and anytime, storing data on secured cloud infrastructure is essential. Cloud services for building Telehealth apps speed up the information exchange and improves the security and privacy controls. One such secured cloud infrastructure is AWS.
AWS provides data security and helps in managing the data with ease. It is HIPAA compliant and hence can be used to run sensitive workloads that are regulated by HIPAA. To include protected health information to AWS service, one of the most important things to do is accepting AWS Business Associate Addendum (BAA). AWS BAA can be used to store, process, and transmit protected health information under HIPAA, which means it can reduce lots of development efforts while assuring data security. Along with security, AWS offers auto scalability to accommodate the real-time dynamic volume of patient requests. This feature is critical as the patient requests might increase or decrease at different points in time during any given day.
Case study: Fully Integrated Telehealth Product Creation
Case study
Fully Integrated Telehealth Product Creation
Problem
The client has a goal to launch a secure Telehealth application across all digital platforms that would help patients connect with the provider with less waiting time and allow providers to offer their services during free hours.
To solve both patient and provider problems, we implemented a user-friendly web and mobile Telehealth application. Patients use this application to consult doctors remotely and by doctors to attend maximum patients based on availability from any place. The provider can use our application either from the mobile or web application, whereas the patient can use it only through the mobile application.
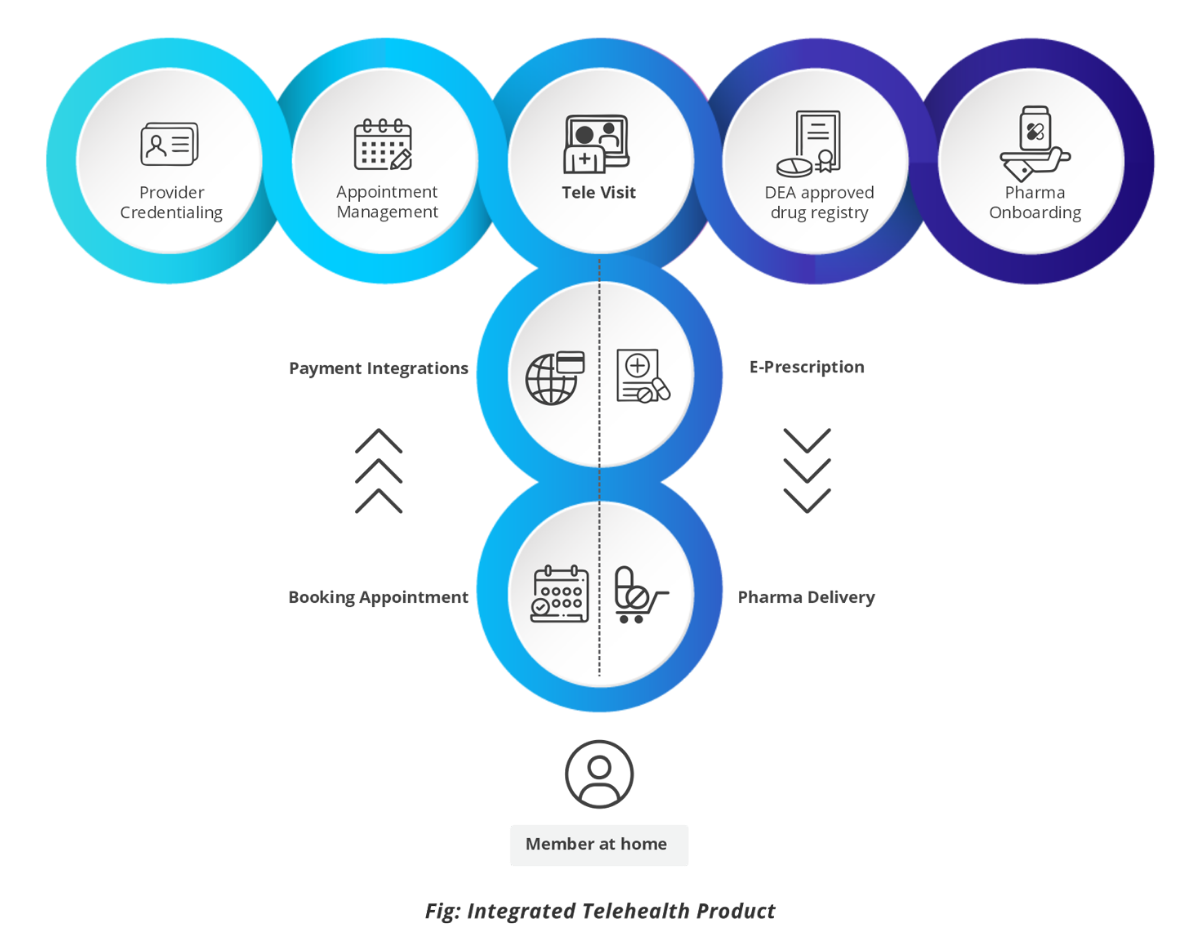
We followed the design thinking approach to derive the customer journey in a typical office visit. We marked the pain point areas that need more attention in a virtual consultation setup based on the traditional process. Our holistic approach brings three key stakeholders on board – Providers, Patients, and Pharmacy stores. With this approach, patients experience a seamless care delivery starting from searching for a provider to receiving the pharmacy medication at home. This application has the following key features:
- Broadcasting patient request for an instant appointment with all available doctor
- Scheduling appointment/call with a preferred provider or any other provider, connecting on call with a provider, and getting the prescription notes from the doctor
- Providing subscription plans to the patient to help patients to consult the doctor with lower costs.
- Helps doctors to attend maximum patients based on availability from any place
- Rating mechanism which is used to improve the service provided to the patients by the provider. (i.e., mapping a patient to a doctor based on the rating of provider and patient)
- Searching nearby pharmacies and ordering the medication prescribed by the doctor during a call.
- An integrated approach to performing provider credentialing as part of onboardin
- Allowing the provider to take notes during the call and send it to the patient post-visit
This robust application can handle all patient operations like onboarding to the application, collecting insurance information and details of pre-existing conditions, scheduling appointments/call with a preferred provider or any available provider, getting call processed for the requested provider, and getting the prescription notes from the doctor.
Provider operations like registering providers, third-party credentialing approval, receiving provider profile information, receiving and accepting patient calls, adding notes while on call, sending prescription for the patient attended, and receiving payment for the service provided can be carried with ease.
The application is designed to handle thousands of patients searching for providers and simultaneously interacting with providers through multiple synchronous threads. To ensure ePHI security, HIPAA guidelines and security protocols were followed during the development.
Conclusion
Conclusion

For a more scalable application, Telehealth requires choosing a secure and cutting-edge technology stack. The development of telemedicine apps involves in-depth technical expertise and extensive knowledge of data compliance. Native mobile apps on iOS and Android platforms are critical to capture an expansive customer base. However, web applications are required for providers to offer virtual consultations as provider offices typically use tabs and desktops.
The competition for leadership on EHR application penetration in the US healthcare market is a good reference for comparing and defining survival strategy for Telehealth application penetration. For the Telehealth applications to thrive, in the world of interoperability, it is very important to have a holistic design with cutting edge technological base that is flexible to accommodate rapid changes and incremental evolution of features.
Post pandemic, a major focus of response efforts by governments and healthcare organizations across the globe, has been on prevention and containment of such threatening health conditions more effectively. Telemedicine systems will be an ideal means for mitigating the overcrowding of hospitals and clinics by triaging low-acuity patients. Further, they can help in preventing unnecessary human exposures and promoting the delivery of high-quality care. State, federal, and international laws and regulations have expanded and amended in recent years, months, and weeks to accommodate greater adoption of telemedicine systems (especially during this public health crisis). EHRs adoption wave and CMS mandates in the US led the traditional healthcare providers to shift focus on embracing technical products as part of their daily operations. Providers are now better position to consider implementing and integrating Telehealth services as a new line of care delivery mechanism.
For Payers, it is essential to create strategic agreements or begin with acquisitions and setup claim reimbursement guidelines to ensure their enrolees are provided with the virtual care delivery model.
For Providers, it is a new, highly lucrative business opportunity that also facilitates optimized provider utilization. Adopting to it quickly would involve a sharp shift in the focus from the traditional models.
For tech companies, this is a potential break in to get a share of US healthcare spending by allowing patients and providers to interact seamlessly and securely across multiple digital platforms.
For CMS, public health is critical, and mandates of adopting Telehealth would mean better preventive care, which in turn, will lead to long-term cost reduction, improved care quality, and timely care to US citizens.
Contributors

Pavan Seepana
Senior Consultant

Agasthya Kommuri
Business Analyst

Nishkala Kollu
Business Analyst
About Innova Solutions
Innova Solutions is a leading global information technology services and consulting organization with 30,000+ employees and has been serving businesses across industries since 1998. A trusted partner to both mid-market and Fortune 500 clients globally, Innova Solutions has been instrumental in each of their unique digital transformation journeys. Our extensive industry-specific expertise and passion for innovation have helped clients envision, build, scale, and run their businesses more efficiently.
We have a proven track record of developing large and complex software and technology solutions for Fortune 500 clients across industries such as Retail, Healthcare & Lifesciences, Manufacturing, Financial Services, Telecom and more. We enable our customers to achieve a digital competitive advantage through flexible and global delivery models, agile methodologies, and battle-proven frameworks. Headquartered in Duluth, GA, and with several locations across North and South America, Europe, and the Asia-Pacific regions, Innova Solutions specializes in 360-degree digital transformation and IT consulting services.
For more information, please reach us at – [email protected]