Strengthening Healthcare Provider Security by Implementing a Vulnerability Remediation Program
October 17, 2023
Outline
In this blog, we intend to address the attack surface for Healthcare Providers with an emphasis on Security Assurance, which addresses the remediation of vulnerabilities across Infrastructure, Network, and Applications to mitigate the risk of exposure to vulnerability exploitation.
Trends in the Healthcare Environment
As per the latest trends, the healthcare industry has been progressively transforming and adopting Digital, Web, and cloud-based technologies to shift towards digitally enabled systems and applications to enhance the quality of healthcare for patients.
However, as the proverb says, ‘Every rose has its thorn.’ Along with the immeasurable benefits that the digital transformation offers, such as information sharing, streamlined operational processes, workflow tracking, enhanced connectivity, and data storage and organizing capabilities, there is also an increased risk of cyberattacks, data breaches, and other related frauds. Consequently, healthcare organizations are highly vulnerable to advanced threats and targeted attacks.
Why are Healthcare Providers a Target for Cybersecurity Attacks?
Utilizing many operational, clinical, and information technology layers leads to an environment that is challenging to maintain, manage, and safeguard. Much like technology, cybersecurity is always changing. To ensure compliance, healthcare organizations should keep themselves abreast of the latest security threats while ensuring compliance. To sum up, healthcare cybersecurity needs to evolve with time.
The newly transformed Digital/Web/Cloud-enabled healthcare environment comprises the following systems and applications.
The table below captures the attack surface associated with the relevant systems and applications:
| Systems & Applications | Attack Surface |
| Electronic Health Record (EHR) Systems: These systems store and process highly sensitive patient information, including medical histories, treatment plans, medications, radiology images, diagnoses, etc. | EHRs are vulnerable to critical security threats due to the abundance of sensitive data they hold and are possible targets of a cyberattack that combines Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS), data leakage, and disruption of patient care. |
| Medical Devices: Medical devices, like infusion pumps, are becoming increasingly connected to the Internet and hence vulnerable to cyberattacks. | Even though a medical device cannot be used to get access to sensitive information, if it is a part of the Internet of Things (IoT), it could potentially be used in a DDoS attack, devastating service-disrupting cyber-attack. |
| Payment Systems: Hospital and medical clinic payment systems are linked to two categories of sought-after data: financial and patient information. | Compromise on payment system led to the loss of Personally Identifiable Information (PII) and credit card information. |
| Websites and Portals: Any web login portal whether it is for patients or medical staff, is a potential gateway to a private network. | If a portal is not secured, it can be manipulated to provide malicious access to sensitive backend databases. |
| Shadow IT: These devices are connected to a network without the consent of security teams, exempting them from the network security policies and their security controls. | Mobile devices used by healthcare professionals are among the most common Shadow IT endpoints that create critical security gaps. |
| Medical Imaging Devices: On-premises devices like MRI machines, X-ray machines, and CT scanners process sensitive imaging data. | Due to the digital management of next-gen devices through a wired or wireless network, a new vector that can be used for intrusion with unpatched vulnerabilities or ineffective system hardening has been created. |
| Digital Appointment Scheduling Systems: Provide users with a seamless interface to schedule, manage, and modify appointments to utilize healthcare services. | If exploited, scheduling apps could act as pathways to access sensitive data or provide hackers with network access sufficient to launch a ransomware attack. |
Contrary to other industries, cybersecurity investments in healthcare have been focused on tools and technology to support vulnerability identification, while remediation of an ever-increasing number of identified vulnerabilities has lagged. Managing the increasing complexity of many servers, endpoints, and applications is challenging.
The value of a health record on the black market has been valued at
$100-$1300
while a social security number is worth less than $20
As of January 2023, HHS Office of Civil
Rights estimates
372,562,469
patient name have reported breeched
Source: https://ocrportal.hhs.gov/ocr/breach/breach_report.jsf
Why Should Healthcare Providers Prioritize Security Assurance?
It’s past time for healthcare organizations to start taking vulnerability management seriously—not just for compliance or cybersecurity reasons but also for the privacy of their patients’ data and, in certain situations, for the safety of their lives.
Organizations should strive for a vulnerability management program that includes identification, assessment, categorization, prioritization, remediation, and mitigation of software vulnerabilities. Healthcare organizations will be able to better manage risk and keep restricted information to themselves and other data secure if they create mature vulnerability management strategies that utilize the appropriate tools and knowledge.
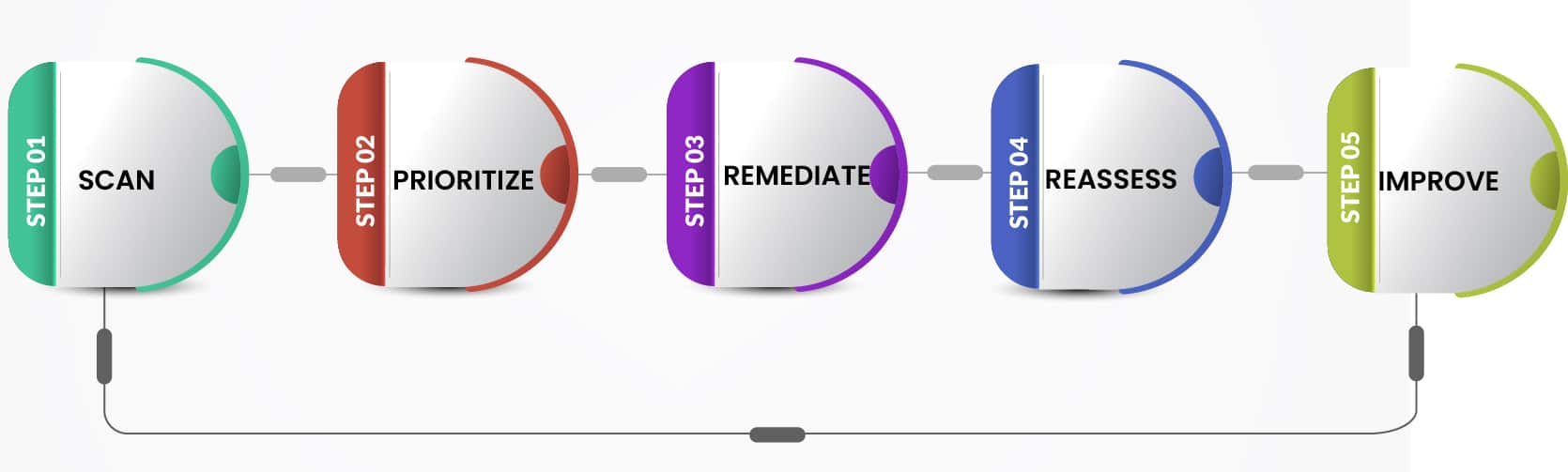
Presenting Innova’s Vulnerability Remediation Program
Scan
- Discovery: Perform network discovery to identify active hosts and services. Identify and catalog all the assets within the defined scope. Determine the scope of the scan, including IP ranges, subnets, and specific applications. Obtain the necessary permissions and approvals to conduct the vulnerability scan.
- Scan Policies: Customize scan parameters, including scan intensity, target ports, and specific vulnerabilities to focus on. Define specific scan policies, such as authenticated scans or unauthenticated scans. Notify relevant stakeholders to minimize disruption and false-positive reports.
- Review Scan Jobs: Monitor the progress and address the issues that may arise during the scan. Re-initiate the scan for the assets that failed the scheduled scan.
- Ad-hoc Scans: Review the requests for ad-hoc scans. Define scan policies to perform authenticated/unauthenticated scans. Notify the stakeholders and execute the scan jobs based on specific scan policies.
Prioritize
- Risk Assessment: After the detection of vulnerabilities, assess the risk associated with each vulnerability. This involves evaluating factors such as the severity of the vulnerability, the potential impact if exploited, and the likelihood of exploitation.
- Prioritization: Prioritize vulnerabilities based on their severity and degree of risk. Focus on addressing critical vulnerabilities with a high likelihood of exploitation first, as they pose the most significant threat to the organization.
- Planning: Based on the report, create a plan to remediate the vulnerabilities. This may involve patching systems, updating software, reconfiguring settings, or implementing additional security measures.
Remediate
- Remediation Testing: Work closely with platform owners to identify the pilot systems across Test, Development, and Production environments and implement remediation controls involving Patches, Configuration changes, updating code, etc. Validate the system/application performance, stability, and document the results covering stability, performance, and behavior. In case there is a noticeable impact, document the same, identify compensating controls, and request for an exception approval. Post-remediation testing, finalize the mass production roll out of remediation controls involving patches, updates, reconfiguration, etc.
- Automated Remediation: Create packages for automated patch rollout, updates, fixes, or reconfiguration settings. Coordinate with the respective stakeholders and finalize the rollout during the maintenance window. Rollout and monitor the remediation status to ensure the complete deployment of remediation recommendations.
- Report: Report remediation status and exceptions to ensure that the CXO(s), Platform Owners, and Business Owners are aware of the Security Posture post-remediation updates encompassing Status of completion, Exceptions Requested, and Compensating Controls.
Reassess
- Post-Remediation Scan: Perform follow-up scans to ensure that the vulnerabilities have been successfully addressed and that no new vulnerabilities have been introduced.
- Report: Report remediation status and exceptions to ensure that the CXO(s), Platform Owners, and Business Owners are aware of the Security Posture post remediation updates covering Status of completion, Exceptions Requested, and Compensating Controls.
Improve
- Service Improvement: Assess & evolve metrics to improve discovery, scanning, analysis, communication, and remediation.
Conclusion
- In the above blog post, we discussed our approach to addressing vulnerability remediation through Innova’s Security Assurance service offerings.
- In the upcoming blog post, we will highlight our strategy around the Cybersecurity Fusion Centre (CFC), its fundamental components, and how the outcomes of Security Assurance bring in the concept of “Proactive” threat management.